The iris in our eyes
What is the iris?
The iris is the colored part of the eye that surrounds the pupil. The iris plays an important role in regulating the incidence of light in the eye and also determines the eye color.
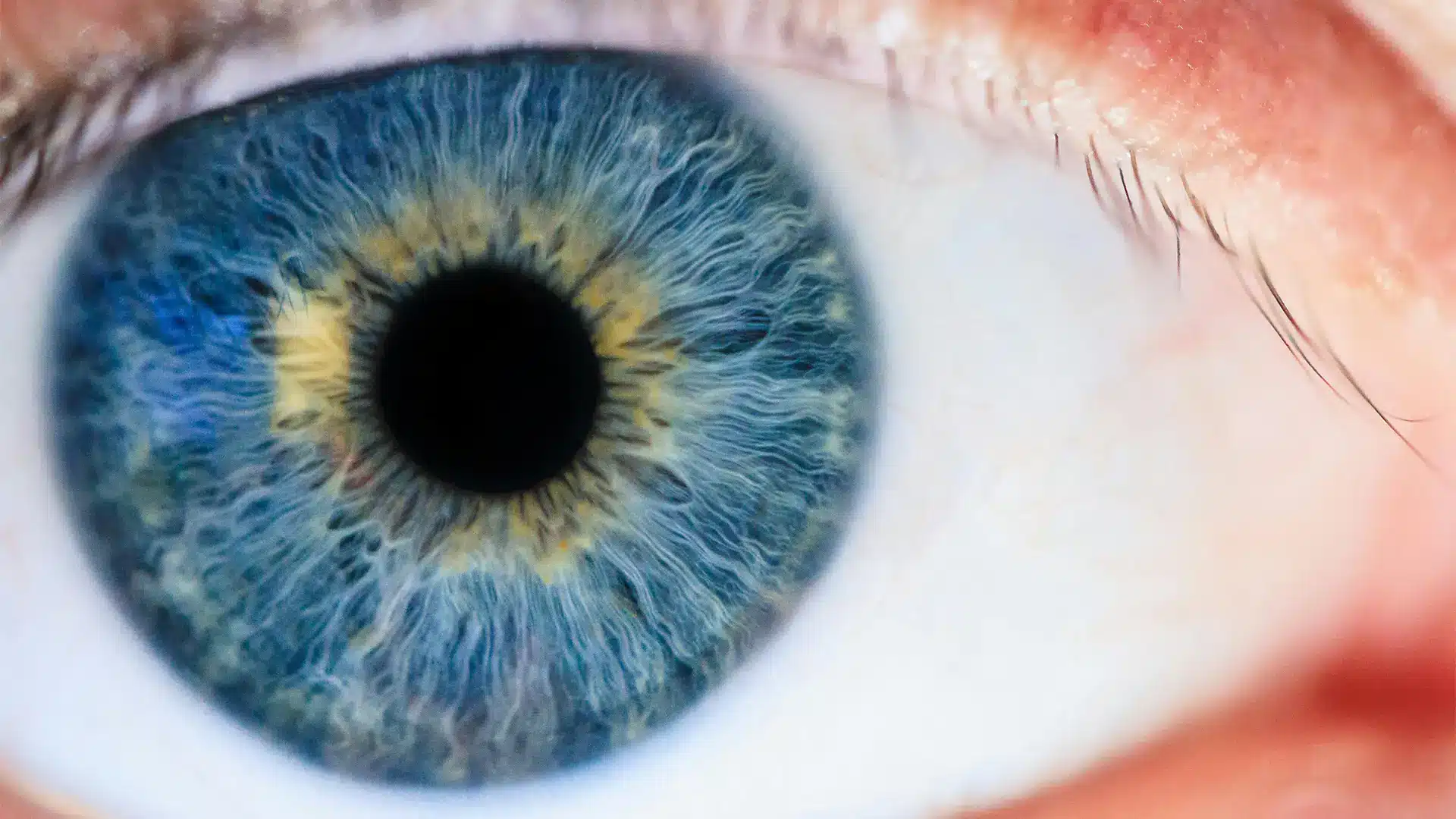
The iris is the colored part of the eye that surrounds the pupil. The iris plays an important role in regulating the incidence of light in the eye and also determines the eye color.
The color of the iris, and therefore the eye color, is determined by the amount and type of pigment called melanin. Melanin is the same pigment that is also responsible for the color of the skin and hair. The main factors that influence eye color are:
Eye color can change in some cases due to age, illness or injury. In babies, the eyes contain little pigment in the first few months. As a result, the eyes are often blue at first and the color changes as they grow older and produce more melanin. After six months, the eye color is usually permanent. Eye color after eyelid surgery The brightness of the iris may subjectively appear to change after eyelid surgery, but this is usually an optical effect caused by changes in how light enters the eye. The procedure itself has no direct effect on the structure or color of the iris.
The window reflex refers to a phenomenon in which light entering through the eyes is reflected by the surface of the eye, specifically the iris. This reflex may become more pronounced after eyelid surgery for a few reasons: